TIGAR (基因名), Fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase TIGAR (蛋白名), tigar_human.
产品名称:
Human TIGAR/ Fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase TIGAR Recombinant Protein
果糖-2,6-二磷酸酶TIGAR
货号:
R5948h
商标:
EIAab®
监管等级:
别名:
TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator, TP53-induced glycolysis regulatory phosphatase, C12orf5
序列号:
Q9NQ88
来源:
E.coli
种属:
Human
标签:
His
序列:
1-270aa
预估分子量:
29.7 kDa (monomer)
纯度:
Greater than 98% by SDS-PAGE
浓度:
Reconstitution Dependent
形态:
Liquid
内毒素水平:
Please contact protein@eiaab.com The technician for more information.
应用:
存储缓冲液:
50mM NaH2PO4, 500mM NaCl Buffer with 500mM Imidazole, 10%glycerol(PH8.0)
存储:
Store at -20°C. (Avoid repeated freezing and thawing.)
研究领域:
-
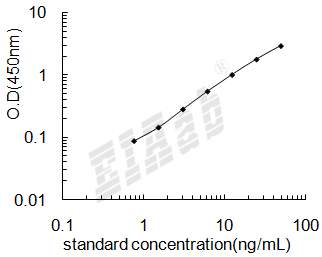
R&D 技术数据
The PCR product of human TIGAR gene was determined by 1% Agarose stained with EB.
Recombinant human TIGAR protein was determined by 12% SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue under reducing conditions.
基因位点
TIGAR Gene in genomic location: bands according to Ensembl, locations according to GeneLoc (and/or Entrez Gene and/or Ensembl if different)
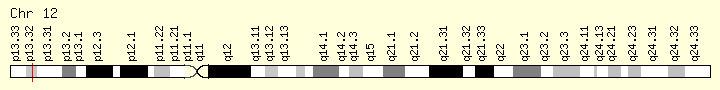
通用注释
亚单元:
Interacts with HK2; the interaction increases hexokinase HK2 activity in a hypoxia- and HIF1A-dependent manner, resulting in the regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential, thus increasing NADPH production and decreasing intracellular ROS levels (PubMed:23185017).
功能:
Fructose-bisphosphatase hydrolyzing fructose-2,6-bisphosphate as well as fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (PubMed:19015259). Acts as a negative regulator of glycolysis by lowering intracellular levels of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate in a p53/TP53-dependent manner, resulting in the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) activation and NADPH production (PubMed:16839880, PubMed:22887998). Contributes to the generation of reduced glutathione to cause a decrease in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) content, correlating with its ability to protect cells from oxidative or metabolic stress-induced cell death (PubMed:16839880, PubMed:19713938, PubMed:23726973, PubMed:22887998, PubMed:23817040). Plays a role in promoting protection against cell death during hypoxia by decreasing mitochondria ROS levels in a HK2-dependent manner through a mechanism that is independent of its fructose-bisphosphatase activity (PubMed:23185017). In response to cardiac damage stress, mediates p53-induced inhibition of myocyte mitophagy through ROS levels reduction and the subsequent inactivation of BNIP3. Reduced mitophagy results in an enhanced apoptotic myocyte cell death, and exacerbates cardiac damage (By similarity). Plays a role in adult intestinal regeneration; contributes to the growth, proliferation and survival of intestinal crypts following tissue ablation (PubMed:23726973). Plays a neuroprotective role against ischemic brain damage by enhancing PPP flux and preserving mitochondria functions (By similarity). Protects glioma cells from hypoxia- and ROS-induced cell death by inhibiting glycolysis and activating mitochondrial energy metabolism and oxygen consumption in a TKTL1-dependent and p53/TP53-independent manner (PubMed:22887998). Plays a role in cancer cell survival by promoting DNA repair through activating PPP flux in a CDK5-ATM-dependent signaling pathway during hypoxia and/or genome stress-induced DNA damage responses (PubMed:25928429). Involved in intestinal tumor progression (PubMed:23726973).
亚细胞位置:
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Mitochondrion
Translocated to the mitochondria during hypoxia in a HIF1A-dependent manner (PubMed:23185017). Colocalizes with HK2 in the mitochondria during hypoxia (PubMed:23185017). Translocated to the nucleus during hypoxia and/or genome stress-induced DNA damage responses in cancer cells (PubMed:25928429). Translocation to the mitochondria is enhanced in ischemic cortex after reperfusion and/or during oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD)/reoxygenation insult in primary neurons (By similarity).
该产品尚未在任何出版物中被引用。
[2].
"TIGAR regulates DNA damage and repair through pentosephosphate pathway and Cdk5-ATM pathway."
[4].
"Knockdown of TIGAR by RNA interference induces apoptosis and autophagy in HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells."
[5].
"Regulatory role of p53 in cancer metabolism via SCO2 and TIGAR in human breast cancer."
[6].
"Tp53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) protects glioma cells from starvation-induced cell death by up-regulating respiration and improving cellular redox homeostasis."
[7].
"Mitochondrial localization of TIGAR under hypoxia stimulates HK2 and lowers ROS and cell death."
[8].
"Structural and biochemical studies of TIGAR (TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator)."
[9].
"Identification of TIGAR in the equilibrative nucleoside transporter 2-mediated response to fludarabine in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells."
[1].
人果糖-2,6-二磷酸酶TIGAR(TIGAR)重组蛋白是否是无菌的?
蛋白试剂瓶和蛋白保存液是经过高压灭菌的,但也不能保证蛋白是完全无菌的。如果要求蛋白是无菌的,可以用0.2微米的滤器对蛋白进行过滤。
[2].
人果糖-2,6-二磷酸酶TIGAR(TIGAR)重组蛋白的保存缓冲液是什么?
纯化后的蛋白保存在PBS(58mM Na2HPO4, 17mM NaH2PO4, 68mM NaCl, pH7.4)里,并往里面加入500mM咪唑和10%甘油。
[3].
怎样确定人果糖-2,6-二磷酸酶TIGAR(TIGAR)重组蛋白的浓度?
蛋白浓度的确定没有一个统一的标准,这主要取决于蛋白的氨基酸序列。伊艾博是根据不同测试的组合来测定蛋白浓度。考马斯亮蓝法、BCA法、氨基酸序列和氨基酸全序列分析法等都用来测定蛋白浓度。
[4].
人果糖-2,6-二磷酸酶TIGAR(TIGAR)重组蛋白蛋白保存条件是怎样的?
蛋白应保存在 -20℃或 -80℃条件下,为了避免反复冻融,可以将蛋白分装成小份保存。
[5].
人果糖-2,6-二磷酸酶TIGAR(TIGAR)重组蛋白是否可以用于活体实验?
重组蛋白没有用于任何的活体实验,因此蛋白的活性和半衰期是不确定的。
[6].
人果糖-2,6-二磷酸酶TIGAR(TIGAR)重组蛋白的保质期是多久?
在适当的保存条件下,从购买之日起蛋白可以稳定保存6-12个月。适当的保存条件是:蛋白保存在-20°C o或 -80℃,保证蛋白的保存浓度高于0.1mg/ml,限制蛋白反复冻融的次数。我们公司常规的质量检测保证所有产品在销售时都有可接受的生物活性。但是我们不能控制终端用户蛋白的保存条件。如果产品在有效期内出现问题,请联系我们的技术支持。
[7].
你们蛋白和抗体的报价是怎么样的?
我们将根据你需要的蛋白和抗体的大小进行报价。
[8].
人果糖-2,6-二磷酸酶TIGAR(TIGAR)重组蛋白是否能够提供蛋白片段?
我们现有的人的蛋白的序列可以有很多。你可以选择你感兴趣的靶向部分,我们将会按您的需求提供蛋白和抗体。
[9].
人果糖-2,6-二磷酸酶TIGAR(TIGAR)重组蛋白的货期或发货时间一般是多长?
具体指标的货期需要确定。最快一周,最长可能一个月。
反馈墙
评论数 : 0
所有用户
所有用户
默认排序
默认排序
最近
早期
目前还没有评论。



通知
规格
数量
单价 (¥)
小计 1 (¥)
小计 2:
¥

规格
数量
单价 (¥)





 验证序列:
验证序列:



 折扣:
折扣: