Mapk14 (基因名), Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 (蛋白名), MK14_RAT.
产品名称:
Rat Mapk14/ Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 ELISA Kit
促分裂原活化蛋白激酶14
货号:
E9114r
商标:
EIAab®
监管等级:
别名:
CRK1, Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 alpha, MAP kinase p38 alpha, MAP kinase 14, Csbp1, Csbp2
检测方法:
ELISA
实验类型:
Sandwich
检测范围:
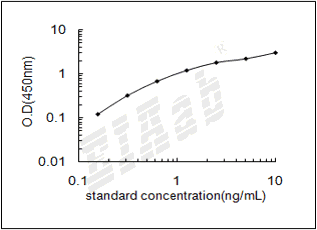
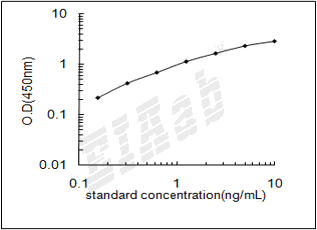
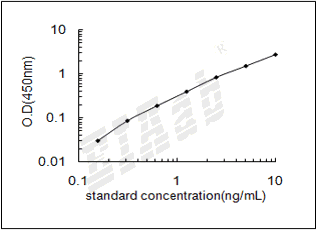
0.156-10ng/mL
灵敏度:
0.078ng/mL
特异性:
Natural and recombinant rat Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14
样品类型:
Serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids
样品数据:
登录.
实验步骤:
研究领域:
Neurosciences
精密度
批内差:已知浓度的3个样本在一个板子内重复检测20次,以评估批内精密度。
批内 CV: ≤4.5%
批间差:已知浓度的3个样本在不同的板子上重复测定5次,以评估测定批间精密度。
批间 CV: ≤9.1%
批内 CV: ≤4.5%
批间差:已知浓度的3个样本在不同的板子上重复测定5次,以评估测定批间精密度。
批间 CV: ≤9.1%
回收率
回收率:低、中和高浓度的分析物被掺入到血清或者血浆样本中,进行回收实验测定。
|
Sample Type |
Average(%) |
Recovery Range(%) |
|
Serum |
97 |
91-103 |
|
Plasma |
99 |
93-105 |
线性
线性:给定样本通过梯度稀释,每次稀释的测量值与理论值的比值。
|
Sample |
1:2 |
1:4 |
1:8 |
1:16 |
|
serum(n=5) |
100-110% |
89-99% |
103-113% |
99-107% |
|
EDTA plasma(n=5) |
105-113% |
100-110% |
87-96% |
102-112% |
|
heparin plasma(n=5) |
91-91%
|
98-108% |
101-110% |
86-98% |
通用注释
亚单元:
Component of a signaling complex containing at least AKAP13, PKN1, MAPK14, ZAK and MAP2K3. Within this complex, AKAP13 interacts directly with PKN1, which in turn recruits MAPK14, MAP2K3 and ZAK (By similarity). Binds to a kinase interaction motif within the protein tyrosine phosphatase, PTPRR (By similarity). This interaction retains MAPK14 in the cytoplasm and prevents nuclear accumulation (By similarity). Interacts with SPAG9 and GADD45A (By similarity). Interacts with CDC25B, CDC25C, DUSP1, DUSP10, DUSP16, NP60, SUPT20H and TAB1. Interacts with casein kinase II subunits CSNK2A1 and CSNK2B. Interacts with PPM1D. Interacts with CDK5RAP3; recruits PPM1D to MAPK14 and may regulate its dephosphorylation.
功能:
Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. MAPK14 is one of the four p38 MAPKs which play an important role in the cascades of cellular responses evoked by extracellular stimuli such as proinflammatory cytokines or physical stress leading to direct activation of transcription factors. Accordingly, p38 MAPKs phosphorylate a broad range of proteins and it has been estimated that they may have approximately 200 to 300 substrates each. Some of the targets are downstream kinases which are activated through phosphorylation and further phosphorylate additional targets. RPS6KA5/MSK1 and RPS6KA4/MSK2 can directly phosphorylate and activate transcription factors such as CREB1, ATF1, the NF-kappa-B isoform RELA/NFKB3, STAT1 and STAT3, but can also phosphorylate histone H3 and the nucleosomal protein HMGN1. RPS6KA5/MSK1 and RPS6KA4/MSK2 play important roles in the rapid induction of immediate-early genes in response to stress or mitogenic stimuli, either by inducing chromatin remodeling or by recruiting the transcription machinery. On the other hand, two other kinase targets, MAPKAPK2/MK2 and MAPKAPK3/MK3, participate in the control of gene expression mostly at the post-transcriptional level, by phosphorylating ZFP36 (tristetraprolin) and ELAVL1, and by regulating EEF2K, which is important for the elongation of mRNA during translation. MKNK1/MNK1 and MKNK2/MNK2, two other kinases activated by p38 MAPKs, regulate protein synthesis by phosphorylating the initiation factor EIF4E2. MAPK14 interacts also with casein kinase II, leading to its activation through autophosphorylation and further phosphorylation of TP53/p53. In the cytoplasm, the p38 MAPK pathway is an important regulator of protein turnover. For example, CFLAR is an inhibitor of TNF-induced apoptosis whose proteasome-mediated degradation is regulated by p38 MAPK phosphorylation. In a similar way, MAPK14 phosphorylates the ubiquitin ligase SIAH2, regulating its activity towards EGLN3. MAPK14 may also inhibit the lysosomal degradation pathway of autophagy by interfering with the intracellular trafficking of the transmembrane protein ATG9. Another function of MAPK14 is to regulate the endocytosis of membrane receptors by different mechanisms that impinge on the small GTPase RAB5A. In addition, clathrin-mediated EGFR internalization induced by inflammatory cytokines and UV irradiation depends on MAPK14-mediated phosphorylation of EGFR itself as well as of RAB5A effectors. Ectodomain shedding of transmembrane proteins is regulated by p38 MAPKs as well. In response to inflammatory stimuli, p38 MAPKs phosphorylate the membrane-associated metalloprotease ADAM17. Such phosphorylation is required for ADAM17-mediated ectodomain shedding of TGF-alpha family ligands, which results in the activation of EGFR signaling and cell proliferation. Another p38 MAPK substrate is FGFR1. FGFR1 can be translocated from the extracellular space into the cytosol and nucleus of target cells, and regulates processes such as rRNA synthesis and cell growth. FGFR1 translocation requires p38 MAPK activation. In the nucleus, many transcription factors are phosphorylated and activated by p38 MAPKs in response to different stimuli. Classical examples include ATF1, ATF2, ATF6, ELK1, PTPRH, DDIT3, TP53/p53 and MEF2C and MEF2A. The p38 MAPKs are emerging as important modulators of gene expression by regulating chromatin modifiers and remodelers. The promoters of several genes involved in the inflammatory response, such as IL6, IL8 and IL12B, display a p38 MAPK-dependent enrichment of histone H3 phosphorylation on 'Ser-10' (H3S10ph) in LPS-stimulated myeloid cells. This phosphorylation enhances the accessibility of the cryptic NF-kappa-B-binding sites marking promoters for increased NF-kappa-B recruitment. Phosphorylates CDC25B and CDC25C which is required for binding to 14-3-3 proteins and leads to initiation of a G2 delay after ultraviolet radiation. Phosphorylates TIAR following DNA damage, releasing TIAR from GADD45A mRNA and preventing mRNA degradation. The p38 MAPKs may also have kinase-independent roles, which are thought to be due to the binding to targets in the absence of phosphorylation. Protein O-Glc-N-acylation catalyzed by the OGT is regulated by MAPK14, and, although OGT does not seem to be phosphorylated by MAPK14, their interaction increases upon MAPK14 activation induced by glucose deprivation. This interaction may regulate OGT activity by recruiting it to specific targets such as neurofilament H, stimulating its O-Glc-N-acylation. Required in mid-fetal development for the growth of embryo-derived blood vessels in the labyrinth layer of the placenta. Also plays an essential role in developmental and stress-induced erythropoiesis, through regulation of EPO gene expression. Phosphorylates S100A9 at 'Thr-113'.
亚细胞位置:
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
该产品尚未在任何出版物中被引用。
[1].
大鼠促分裂原活化蛋白激酶14(Mapk14)ELISA试剂盒可以做多少个样本?
大鼠促分裂原活化蛋白激酶14(Mapk14)ELISA试剂盒分为2种规格,96孔和48孔。96孔的试剂盒,标曲和样本都做复孔的话,可以检测40个样本。96孔的试剂盒,标曲和样本都不做复孔的话,可以检测88个样本。
[2].
大鼠促分裂原活化蛋白激酶14(Mapk14)ELISA试剂盒使用视频?
大鼠促分裂原活化蛋白激酶14(Mapk14)ELISA试剂盒实验操作视频在以下网址中,对每一步的实验步骤都做了演示,方便实验员能更好地理解ELISA实验的过程。
https://www.eiaab.com.cn/lesson-tech/805.html
https://www.eiaab.com.cn/lesson-tech/805.html
[3].
大鼠促分裂原活化蛋白激酶14(Mapk14)ELISA试剂盒是放在-20℃冰箱保存吗?
EIAab的大鼠促分裂原活化蛋白激酶14(Mapk14)ELISA试剂盒,洗涤液、底物、终止液保存于4℃,其余试剂-20℃冰箱保存。
[4].
大鼠促分裂原活化蛋白激酶14(Mapk14)ELISA试剂盒原理?
双抗体夹心法:用纯化的抗体包被微孔板,制成固相抗体,往包被有固相抗体的微孔中依次加入标准品或受检样本、生物素化抗体、HRP标记的亲和素,经过彻底洗涤后用底物TMB显色。用酶标仪在450nm波长下测定吸光度(OD值),计算样本浓度。
竞争法:用纯化的抗体包被微孔板,制成固相抗体,往包被有固相抗体的微孔中依次加入标准品或受检样本和生物素标记的目标分析物,受检标本中抗原与生物素标记抗原竞争结合有限的抗体。再加入HRP标记的亲和素,经过彻底洗涤后用底物TMB显色。用酶标仪在450nm波长下测定吸光度(OD值),计算样本浓度。
竞争法:用纯化的抗体包被微孔板,制成固相抗体,往包被有固相抗体的微孔中依次加入标准品或受检样本和生物素标记的目标分析物,受检标本中抗原与生物素标记抗原竞争结合有限的抗体。再加入HRP标记的亲和素,经过彻底洗涤后用底物TMB显色。用酶标仪在450nm波长下测定吸光度(OD值),计算样本浓度。
[5].
大鼠促分裂原活化蛋白激酶14(Mapk14)ELISA试剂盒中需要使用的样品量是多少?
夹心法100μL/孔,竞争法50μL/孔。如样本浓度过高时,应对样本进行稀释,以使稀释后的样本符合试剂盒的检测范围,计算时再乘以相应的稀释倍数。
[6].
如何分析大鼠促分裂原活化蛋白激酶14(Mapk14)ELISA试剂盒数据?
建议标准曲线,并计算样本浓度。对于elisa的曲线拟合,一般建议采用4参数曲线拟合,4参数曲线拟合通常更适合免疫分析。推荐使用专业软件进行曲线拟合,例如curve expert 1.3。根据样本的OD值由标曲查出相应的浓度,再乘以稀释倍数;或用标准物的浓度与OD值计算出标曲的回归方程式,将样本的OD值代入方程式,计算出样本浓度,再乘以稀释倍数,即为样本的实际浓度。以下链接是curve expert 1.3软件拟合曲线的方法。
https://www.eiaab.com.cn/news/502/
https://www.eiaab.com.cn/news/502/
[7].
大鼠促分裂原活化蛋白激酶14(Mapk14)ELISA试剂盒中是否包含人和动物的副产物,是否包含感染的或者传染性原料如HIV等?
除了抗体和稀释液中的BSA,不含其它人和动物的副产物,也不含感染材料。
[8].
收集大鼠促分裂原活化蛋白激酶14(Mapk14)ELISA试剂盒血浆样本,用什么作为抗凝剂?
一般建议用EDTA和肝素作为抗凝剂。
[9].
大鼠促分裂原活化蛋白激酶14(Mapk14)ELISA试剂盒酶标板可以拆成几部分?拆的时候是否需要避光,无菌?
大鼠促分裂原活化蛋白激酶14(Mapk14)ELISA试剂盒酶标板是8×12孔条,可拆卸,板子可以拆成12条,注意避免孔污染,不需要避光和无菌。暂时不用的板子,放回原来装的袋子里,密封保存。
[10].
大鼠促分裂原活化蛋白激酶14(Mapk14)ELISA试剂盒样本如何保存?
尽量检测新鲜样本。若无新鲜样本,则4℃保存1周,-20℃保存1个月,-80℃保存2个月。
反馈墙
评论数 : 0
所有用户
所有用户
默认排序
默认排序
最近
早期
目前还没有评论。



通知
规格
数量
单价 (¥)
小计 1 (¥)
小计 2:
¥

规格
数量
单价 (¥)





 验证序列:
验证序列:



 折扣:
折扣: