Acta2 (基因名), Actin, aortic smooth muscle (蛋白名), ACTA_RAT.
产品名称:
Rat Acta2/ Actin, aortic smooth muscle ELISA Kit
肌动蛋白,主动脉平滑肌
货号:
E1342r
商标:
EIAab®
监管等级:
别名:
Alpha-actin-2, Actsa, Actvs
检测方法:
ELISA
实验类型:
Sandwich
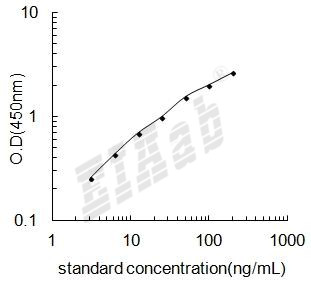
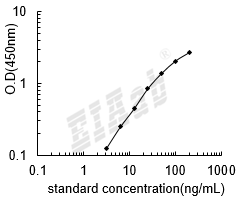
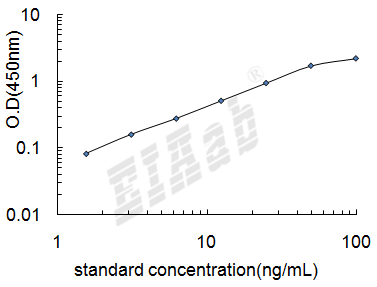
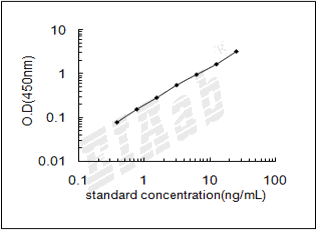
检测范围:
3.12-200ng/mL
灵敏度:
1.56ng/mL
特异性:
Natural and recombinant rat Actin, aortic smooth muscle
样品类型:
Serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids
样品数据:
登录.
实验步骤:
研究领域:
-
通用注释
亚单元:
Polymerization of globular actin (G-actin) leads to a structural filament (F-actin) in the form of a two-stranded helix. Each actin can bind to 4 others.
功能:
Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells.
亚细胞位置:
Cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton
该产品尚未在任何出版物中被引用。
[1].
大鼠肌动蛋白,主动脉平滑肌(Acta2)ELISA试剂盒可以做多少个样本?
大鼠肌动蛋白,主动脉平滑肌(Acta2)ELISA试剂盒分为2种规格,96孔和48孔。96孔的试剂盒,标曲和样本都做复孔的话,可以检测40个样本。96孔的试剂盒,标曲和样本都不做复孔的话,可以检测88个样本。
[2].
大鼠肌动蛋白,主动脉平滑肌(Acta2)ELISA试剂盒使用视频?
大鼠肌动蛋白,主动脉平滑肌(Acta2)ELISA试剂盒实验操作视频在以下网址中,对每一步的实验步骤都做了演示,方便实验员能更好地理解ELISA实验的过程。
https://www.eiaab.com.cn/lesson-tech/805.html
https://www.eiaab.com.cn/lesson-tech/805.html
[3].
大鼠肌动蛋白,主动脉平滑肌(Acta2)ELISA试剂盒是放在-20℃冰箱保存吗?
EIAab的大鼠肌动蛋白,主动脉平滑肌(Acta2)ELISA试剂盒,洗涤液、底物、终止液保存于4℃,其余试剂-20℃冰箱保存。
[4].
大鼠肌动蛋白,主动脉平滑肌(Acta2)ELISA试剂盒原理?
双抗体夹心法:用纯化的抗体包被微孔板,制成固相抗体,往包被有固相抗体的微孔中依次加入标准品或受检样本、生物素化抗体、HRP标记的亲和素,经过彻底洗涤后用底物TMB显色。用酶标仪在450nm波长下测定吸光度(OD值),计算样本浓度。
竞争法:用纯化的抗体包被微孔板,制成固相抗体,往包被有固相抗体的微孔中依次加入标准品或受检样本和生物素标记的目标分析物,受检标本中抗原与生物素标记抗原竞争结合有限的抗体。再加入HRP标记的亲和素,经过彻底洗涤后用底物TMB显色。用酶标仪在450nm波长下测定吸光度(OD值),计算样本浓度。
竞争法:用纯化的抗体包被微孔板,制成固相抗体,往包被有固相抗体的微孔中依次加入标准品或受检样本和生物素标记的目标分析物,受检标本中抗原与生物素标记抗原竞争结合有限的抗体。再加入HRP标记的亲和素,经过彻底洗涤后用底物TMB显色。用酶标仪在450nm波长下测定吸光度(OD值),计算样本浓度。
[5].
大鼠肌动蛋白,主动脉平滑肌(Acta2)ELISA试剂盒中需要使用的样品量是多少?
夹心法100μL/孔,竞争法50μL/孔。如样本浓度过高时,应对样本进行稀释,以使稀释后的样本符合试剂盒的检测范围,计算时再乘以相应的稀释倍数。
[6].
如何分析大鼠肌动蛋白,主动脉平滑肌(Acta2)ELISA试剂盒数据?
建议标准曲线,并计算样本浓度。对于elisa的曲线拟合,一般建议采用4参数曲线拟合,4参数曲线拟合通常更适合免疫分析。推荐使用专业软件进行曲线拟合,例如curve expert 1.3。根据样本的OD值由标曲查出相应的浓度,再乘以稀释倍数;或用标准物的浓度与OD值计算出标曲的回归方程式,将样本的OD值代入方程式,计算出样本浓度,再乘以稀释倍数,即为样本的实际浓度。以下链接是curve expert 1.3软件拟合曲线的方法。
https://www.eiaab.com.cn/news/502/
https://www.eiaab.com.cn/news/502/
[7].
大鼠肌动蛋白,主动脉平滑肌(Acta2)ELISA试剂盒中是否包含人和动物的副产物,是否包含感染的或者传染性原料如HIV等?
除了抗体和稀释液中的BSA,不含其它人和动物的副产物,也不含感染材料。
[8].
收集大鼠肌动蛋白,主动脉平滑肌(Acta2)ELISA试剂盒血浆样本,用什么作为抗凝剂?
一般建议用EDTA和肝素作为抗凝剂。
[9].
大鼠肌动蛋白,主动脉平滑肌(Acta2)ELISA试剂盒酶标板可以拆成几部分?拆的时候是否需要避光,无菌?
大鼠肌动蛋白,主动脉平滑肌(Acta2)ELISA试剂盒酶标板是8×12孔条,可拆卸,板子可以拆成12条,注意避免孔污染,不需要避光和无菌。暂时不用的板子,放回原来装的袋子里,密封保存。
[10].
大鼠肌动蛋白,主动脉平滑肌(Acta2)ELISA试剂盒样本如何保存?
尽量检测新鲜样本。若无新鲜样本,则4℃保存1周,-20℃保存1个月,-80℃保存2个月。
反馈墙
评论数 : 0
所有用户
所有用户
默认排序
默认排序
最近
早期
目前还没有评论。



通知
规格
数量
单价 (¥)
小计 1 (¥)
小计 2:
¥

规格
数量
单价 (¥)





 验证序列:
验证序列:



 折扣:
折扣: