EIF4EBP2 (基因名), Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 2 (蛋白名), 4EBP2_HUMAN.
产品名称:
Human EIF4EBP2/ Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 2 ELISA Kit
真核翻译起始因子4e结合蛋白2
货号:
E2694h
商标:
EIAab®
监管等级:
别名:
4E-BP2
检测方法:
ELISA
实验类型:
Sandwich
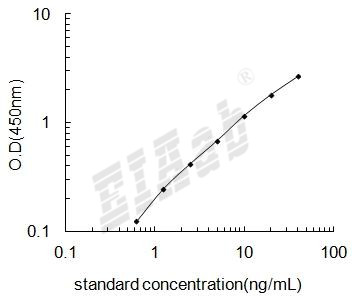
检测范围:
0.625-40ng/mL
灵敏度:
0.265ng/mL
特异性:
Natural and recombinant human Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 2
样品类型:
Serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids
样品数据:
登录.
实验步骤:
研究领域:
-
通用注释
亚单元:
Hypophosphorylated EIF4EBP2 interacts with EIF4E; phosphorylation of EIF4EBP2 by mTORC1 causes dissociation of the complex allowing EIF4G1/EIF4G3 to bind and consequent initiation of translation (PubMed:7935836, PubMed:24207126, PubMed:21661078, PubMed:25533957). Interacts with RPTOR; promoting phosphorylation by mTORC1 (By similarity). Interacts with PCMT1; required to prevent isoaspartate accumulation and convert isoaspartate to Asp.
功能:
Repressor of translation initiation involved in synaptic plasticity, learning and memory formation (By similarity). Regulates EIF4E activity by preventing its assembly into the eIF4F complex: hypophosphorylated form of EIF4EBP2 competes with EIF4G1/EIF4G3 and strongly binds to EIF4E, leading to repress translation. In contrast, hyperphosphorylated form dissociates from EIF4E, allowing interaction between EIF4G1/EIF4G3 and EIF4E, leading to initiation of translation (PubMed:25533957). EIF4EBP2 is enriched in brain and acts as a regulator of synapse activity and neuronal stem cell renewal via its ability to repress translation initiation (By similarity). Mediates the regulation of protein translation by hormones, growth factors and other stimuli that signal through the MAP kinase and mTORC1 pathways.
亚细胞位置:
N/A
该产品尚未在任何出版物中被引用。
[1].
人真核翻译起始因子4e结合蛋白2(EIF4EBP2)ELISA试剂盒可以做多少个样本?
人真核翻译起始因子4e结合蛋白2(EIF4EBP2)ELISA试剂盒分为2种规格,96孔和48孔。96孔的试剂盒,标曲和样本都做复孔的话,可以检测40个样本。96孔的试剂盒,标曲和样本都不做复孔的话,可以检测88个样本。
[2].
人真核翻译起始因子4e结合蛋白2(EIF4EBP2)ELISA试剂盒使用视频?
人真核翻译起始因子4e结合蛋白2(EIF4EBP2)ELISA试剂盒实验操作视频在以下网址中,对每一步的实验步骤都做了演示,方便实验员能更好地理解ELISA实验的过程。
https://www.eiaab.com.cn/lesson-tech/805.html
https://www.eiaab.com.cn/lesson-tech/805.html
[3].
人真核翻译起始因子4e结合蛋白2(EIF4EBP2)ELISA试剂盒是放在-20℃冰箱保存吗?
EIAab的人真核翻译起始因子4e结合蛋白2(EIF4EBP2)ELISA试剂盒,洗涤液、底物、终止液保存于4℃,其余试剂-20℃冰箱保存。
[4].
人真核翻译起始因子4e结合蛋白2(EIF4EBP2)ELISA试剂盒原理?
双抗体夹心法:用纯化的抗体包被微孔板,制成固相抗体,往包被有固相抗体的微孔中依次加入标准品或受检样本、生物素化抗体、HRP标记的亲和素,经过彻底洗涤后用底物TMB显色。用酶标仪在450nm波长下测定吸光度(OD值),计算样本浓度。
竞争法:用纯化的抗体包被微孔板,制成固相抗体,往包被有固相抗体的微孔中依次加入标准品或受检样本和生物素标记的目标分析物,受检标本中抗原与生物素标记抗原竞争结合有限的抗体。再加入HRP标记的亲和素,经过彻底洗涤后用底物TMB显色。用酶标仪在450nm波长下测定吸光度(OD值),计算样本浓度。
竞争法:用纯化的抗体包被微孔板,制成固相抗体,往包被有固相抗体的微孔中依次加入标准品或受检样本和生物素标记的目标分析物,受检标本中抗原与生物素标记抗原竞争结合有限的抗体。再加入HRP标记的亲和素,经过彻底洗涤后用底物TMB显色。用酶标仪在450nm波长下测定吸光度(OD值),计算样本浓度。
[5].
人真核翻译起始因子4e结合蛋白2(EIF4EBP2)ELISA试剂盒中需要使用的样品量是多少?
夹心法100μL/孔,竞争法50μL/孔。如样本浓度过高时,应对样本进行稀释,以使稀释后的样本符合试剂盒的检测范围,计算时再乘以相应的稀释倍数。
[6].
如何分析人真核翻译起始因子4e结合蛋白2(EIF4EBP2)ELISA试剂盒数据?
建议标准曲线,并计算样本浓度。对于elisa的曲线拟合,一般建议采用4参数曲线拟合,4参数曲线拟合通常更适合免疫分析。推荐使用专业软件进行曲线拟合,例如curve expert 1.3。根据样本的OD值由标曲查出相应的浓度,再乘以稀释倍数;或用标准物的浓度与OD值计算出标曲的回归方程式,将样本的OD值代入方程式,计算出样本浓度,再乘以稀释倍数,即为样本的实际浓度。以下链接是curve expert 1.3软件拟合曲线的方法。
https://www.eiaab.com.cn/news/502/
https://www.eiaab.com.cn/news/502/
[7].
人真核翻译起始因子4e结合蛋白2(EIF4EBP2)ELISA试剂盒中是否包含人和动物的副产物,是否包含感染的或者传染性原料如HIV等?
除了抗体和稀释液中的BSA,不含其它人和动物的副产物,也不含感染材料。
[8].
收集人真核翻译起始因子4e结合蛋白2(EIF4EBP2)ELISA试剂盒血浆样本,用什么作为抗凝剂?
一般建议用EDTA和肝素作为抗凝剂。
[9].
人真核翻译起始因子4e结合蛋白2(EIF4EBP2)ELISA试剂盒酶标板可以拆成几部分?拆的时候是否需要避光,无菌?
人真核翻译起始因子4e结合蛋白2(EIF4EBP2)ELISA试剂盒酶标板是8×12孔条,可拆卸,板子可以拆成12条,注意避免孔污染,不需要避光和无菌。暂时不用的板子,放回原来装的袋子里,密封保存。
[10].
人真核翻译起始因子4e结合蛋白2(EIF4EBP2)ELISA试剂盒样本如何保存?
尽量检测新鲜样本。若无新鲜样本,则4℃保存1周,-20℃保存1个月,-80℃保存2个月。
反馈墙
评论数 : 0
所有用户
所有用户
默认排序
默认排序
最近
早期
目前还没有评论。



通知
规格
数量
单价 (¥)
小计 1 (¥)
小计 2:
¥

规格
数量
单价 (¥)





 验证序列:
验证序列:



 折扣:
折扣: