Kcna1 (基因名), Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 1 (蛋白名), kcna1_mouse.
产品名称:
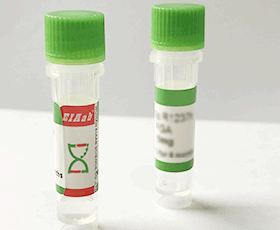
Mouse Kcna1/ Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 1 Recombinant Protein
货号:
-
商标:
EIAab®
监管等级:
别名:
MBK1, MKI, Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv1.1
序列号:
P16388
来源:
E.coli
种属:
Mouse
标签:
His
纯度:
>90% by SDS-PAGE
浓度:
Reconstitution Dependent
形态:
Liquid
内毒素水平:
Please contact protein@eiaab.com The technician for more information.
应用:
存储缓冲液:
50mM NaH2PO4, 500mM NaCl Buffer with 500mM Imidazole, 10%glycerol(PH8.0)
存储:
Store at -20°C. (Avoid repeated freezing and thawing.)
研究领域:
Neurosciences
通用注释
亚单元:
Homotetramer and heterotetramer with other channel-forming alpha subunits, such as KCNA2, KCNA4, KCNA5, KCNA6 and KCNA7 (PubMed:8361541). Channel activity is regulated by interaction with the beta subunits KCNAB1 and KCNAB2 (PubMed:15361858). Identified in a complex with KCNA2 and KCNAB2. Interacts (via C-terminus) with the PDZ domains of DLG1, DLG2 and DLG4 (By similarity). Interacts with LGI1 within a complex containing LGI1, KCNA4 and KCNAB1 (By similarity). Interacts (via N-terminus) with STX1A; this promotes channel inactivation (By similarity). Interacts (via N-terminus) with the heterodimer formed by GNB1 and GNG2; this promotes channel inactivation (By similarity). Can interact simultaneously with STX1A and the heterodimer formed by GNB1 and GNG2 (By similarity). Interacts (via cytoplasmic N-terminal domain) with KCNRG; this inhibits channel activity (By similarity). Interacts with ANK3; this inhibits channel activity (PubMed:23903368).
功能:
Voltage-gated potassium channel that mediates transmembrane potassium transport in excitable membranes, primarily in the brain and the central nervous system, but also in the kidney. Contributes to the regulation of the membrane potential and nerve signaling, and prevents neuronal hyperexcitability (PubMed:9736643, PubMed:9581771 PubMed:10191303, PubMed:12611922, PubMed:21966978, PubMed:22158511, PubMed:23473320). Forms tetrameric potassium-selective channels through which potassium ions pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. The channel alternates between opened and closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane (PubMed:15361858). Can form functional homotetrameric channels and heterotetrameric channels that contain variable proportions of KCNA1, KCNA2, KCNA4, KCNA5, KCNA6, KCNA7, and possibly other family members as well; channel properties depend on the type of alpha subunits that are part of the channel. Channel properties are modulated by cytoplasmic beta subunits that regulate the subcellular location of the alpha subunits and promote rapid inactivation of delayed rectifier potassium channels (PubMed:15361858). In vivo, membranes probably contain a mixture of heteromeric potassium channel complexes, making it difficult to assign currents observed in intact tissues to any particular potassium channel family member. Homotetrameric KCNA1 forms a delayed-rectifier potassium channel that opens in response to membrane depolarization, followed by slow spontaneous channel closure (PubMed:7517498, PubMed:15361858). In contrast, a heterotetrameric channel formed by KCNA1 and KCNA4 shows rapid inactivation (By similarity). Regulates neuronal excitability in hippocampus, especially in mossy fibers and medial perforant path axons, preventing neuronal hyperexcitability (PubMed:23466697). May function as down-stream effector for G protein-coupled receptors and inhibit GABAergic inputs to basolateral amygdala neurons (By similarity). May contribute to the regulation of neurotransmitter release, such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) release (By similarity). Plays a role in regulating the generation of action potentials and preventing hyperexcitability in myelinated axons of the vagus nerve, and thereby contributes to the regulation of heart contraction (PubMed:20392939, PubMed:22641786, PubMed:25377007). Required for normal neuromuscular responses (PubMed:9736643). Regulates the frequency of neuronal action potential firing in response to mechanical stimuli, and plays a role in the perception of pain caused by mechanical stimuli, but does not play a role in the perception of pain due to heat stimuli (PubMed:23473320). Required for normal responses to auditory stimuli and precise location of sound sources, but not for sound perception (PubMed:21966978, PubMed:22396426). The use of toxins that block specific channels suggest that it contributes to the regulation of the axonal release of the neurotransmitter dopamine (PubMed:21233214). Required for normal postnatal brain development and normal proliferation of neuronal precursor cells in the brain (PubMed:8995755, PubMed:17250763, PubMed:17315199, PubMed:22411008). Plays a role in the reabsorption of Mg(2+) in the distal convoluted tubules in the kidney and in magnesium ion homeostasis, probably via its effect on the membrane potential.
亚细胞位置:
Cell membrane
Multi-pass membrane protein
Cell projection
Axon
Membrane
Perikaryon
Cell projection
Dendrite
Cell junction
Cell junction
Synapse
Cytoplasmic vesicle
Endoplasmic reticulum
Cell junction
Synapse
Presynaptic cell membrane
Homotetrameric KCNA1 is primarily located in the endoplasmic reticulum. Interaction with KCNA2 and KCNAB2 or with KCNA4 and KCNAB2 promotes expression at the cell membrane (By similarity). Detected at axon terminals (PubMed:21233214).
数据库链接
您可能感兴趣
该产品尚未在任何出版物中被引用。
[1].
小鼠Kcna1重组蛋白是否是无菌的?
蛋白试剂瓶和蛋白保存液是经过高压灭菌的,但也不能保证蛋白是完全无菌的。如果要求蛋白是无菌的,可以用0.2微米的滤器对蛋白进行过滤。
[2].
小鼠Kcna1重组蛋白的保存缓冲液是什么?
纯化后的蛋白保存在PBS(58mM Na2HPO4, 17mM NaH2PO4, 68mM NaCl, pH7.4)里,并往里面加入500mM咪唑和10%甘油。
[3].
怎样确定小鼠Kcna1重组蛋白的浓度?
蛋白浓度的确定没有一个统一的标准,这主要取决于蛋白的氨基酸序列。伊艾博是根据不同测试的组合来测定蛋白浓度。考马斯亮蓝法、BCA法、氨基酸序列和氨基酸全序列分析法等都用来测定蛋白浓度。
[4].
小鼠Kcna1重组蛋白蛋白保存条件是怎样的?
蛋白应保存在 -20℃或 -80℃条件下,为了避免反复冻融,可以将蛋白分装成小份保存。
[5].
小鼠Kcna1重组蛋白是否可以用于活体实验?
重组蛋白没有用于任何的活体实验,因此蛋白的活性和半衰期是不确定的。
[6].
小鼠Kcna1重组蛋白的保质期是多久?
在适当的保存条件下,从购买之日起蛋白可以稳定保存6-12个月。适当的保存条件是:蛋白保存在-20°C o或 -80℃,保证蛋白的保存浓度高于0.1mg/ml,限制蛋白反复冻融的次数。我们公司常规的质量检测保证所有产品在销售时都有可接受的生物活性。但是我们不能控制终端用户蛋白的保存条件。如果产品在有效期内出现问题,请联系我们的技术支持。
[7].
你们蛋白和抗体的报价是怎么样的?
我们将根据你需要的蛋白和抗体的大小进行报价。
[8].
小鼠Kcna1重组蛋白是否能够提供蛋白片段?
我们现有的人的蛋白的序列可以有很多。你可以选择你感兴趣的靶向部分,我们将会按您的需求提供蛋白和抗体。
[9].
小鼠Kcna1重组蛋白的货期或发货时间一般是多长?
具体指标的货期需要确定。最快一周,最长可能一个月。
反馈墙
评论数 : 0
所有用户
所有用户
默认排序
默认排序
最近
早期
目前还没有评论。



通知
规格
数量
单价 (¥)
小计 1 (¥)
小计 2:
¥

规格
数量
单价 (¥)




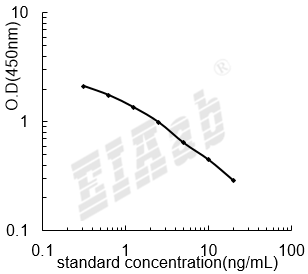
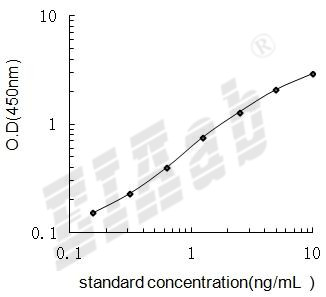
 验证序列:
验证序列:



 折扣:
折扣: