CGAS (基因名), Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (蛋白名), cgas_pig.
产品名称:
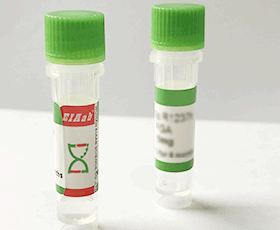
Pig CGAS/ Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase Recombinant Protein
循环GMP-AMP合酶
货号:
R15566p
商标:
EIAab®
监管等级:
别名:
2'3'-cGAMP synthase, Mab-21 domain-containing protein 1, cGAMP synthase, MB21D1
序列号:
I3LM39
来源:
E.coli
种属:
Pig
标签:
His
纯度:
>90% by SDS-PAGE
浓度:
Reconstitution Dependent
形态:
Liquid
内毒素水平:
Please contact protein@eiaab.com The technician for more information.
应用:
存储缓冲液:
50mM NaH2PO4, 500mM NaCl Buffer with 500mM Imidazole, 10%glycerol(PH8.0)
存储:
Store at -20°C. (Avoid repeated freezing and thawing.)
研究领域:
-
R&D 技术数据
更多信息,请参阅手册,或联系我们的技术支持: tech@eiaab.com.
通用注释
亚单元:
Monomer in the absence of DNA. Homodimer in presence of dsDNA: forms a 2:2 dimer with two enzymes binding to two DNA molecules (By similarity). Interacts with PQBP1 (via WW domain). Interacts with TRIM14; this interaction stabilizes CGAS and promotes type I interferon production. Interacts with ZCCHC3; promoting sensing of dsDNA by CGAS. Interacts with PARP1; interaction takes place in the nucleus and prevents the formation of the PARP1-TIMELESS complex (By similarity).
功能:
Nucleotidyltransferase that catalyzes the formation of cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) from ATP and GTP and plays a key role in innate immunity (PubMed:23722159). Catalysis involves both the formation of a 2',5' phosphodiester linkage at the GpA step and the formation of a 3',5' phosphodiester linkage at the ApG step, producing c[G(2',5')pA(3',5')p] (PubMed:23722159). Acts as a key cytosolic DNA sensor, the presence of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) in the cytoplasm being a danger signal that triggers the immune responses. Binds cytosolic DNA directly, leading to activation and synthesis of cGAMP, a second messenger that binds to and activates TMEM173/STING, thereby triggering type-I interferon production. Preferentially binds long dsDNA (around 45 bp) and forms ladder-like networks that function cooperatively to stabilize individual cGAS-dsDNA complexes. Has antiviral activity by sensing the presence of dsDNA from DNA viruses in the cytoplasm. Also acts as an innate immune sensor of infection by retroviruses by detecting the presence of reverse-transcribed DNA in the cytosol. Detection of retroviral reverse-transcribed DNA in the cytosol may be indirect and be mediated via interaction with PQBP1, which directly binds reverse-transcribed retroviral DNA. Also detects the presence of DNA from bacteria. cGAMP can be transferred from producing cells to neighboring cells through gap junctions, leading to promote TMEM173/STING activation and convey immune response to connecting cells. cGAMP can also be transferred between cells by virtue of packaging within viral particles contributing to IFN-induction in newly infected cells in a cGAS-independent but TMEM173/STING-dependent manner. In addition to antiviral activity, also involved in the response to cellular stresses, such as senescence, DNA damage or genome instability. Acts as a regulator of cellular senescence by binding to cytosolic chromatin fragments that are present in senescent cells, leading to trigger type-I interferon production via TMEM173/STING and promote cellular senescence. Also involved in the inflammatory response to genome instability and double-stranded DNA breaks: acts by localizing to micronuclei arising from genome instability. Micronuclei, which as frequently found in cancer cells, consist of chromatin surrounded by its own nuclear membrane: following breakdown of the micronuclear envelope, a process associated with chromothripsis, CGAS binds self-DNA exposed to the cytosol, leading to cGAMP synthesis and subsequent activation of TMEM173/STING and type-I interferon production. Acts as a suppressor of DNA repair in response to DNA damage: translocates to the nucleus following dephosphorylation at Tyr-190 and inhibits homologous recombination repair by interacting with PARP1, the CGAS-PARP1 interaction leading to impede the formation of the PARP1-TIMELESS complex (By similarity).
亚细胞位置:
Cell membrane
Peripheral membrane protein
Cytoplasm
Cytosol
Nucleus
In resting conditions, localizes at the cell membrane as a peripheral membrane protein by binding to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2). Localization at the cell membrane is required to limit the recognition of self-DNA. Following detection of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), released from the cell membrane into the cytosol in order to signal. Upon transfection with dsDNA forms punctate structures that co-localize with DNA and Beclin-1 (BECN1). Phosphorylation at Tyr-190 promotes cytosolic retention; translocates into the nucleus following dephosphorylation.
该产品尚未在任何出版物中被引用。
[1].
猪循环GMP-AMP合酶(CGAS)重组蛋白是否是无菌的?
蛋白试剂瓶和蛋白保存液是经过高压灭菌的,但也不能保证蛋白是完全无菌的。如果要求蛋白是无菌的,可以用0.2微米的滤器对蛋白进行过滤。
[2].
猪循环GMP-AMP合酶(CGAS)重组蛋白的保存缓冲液是什么?
纯化后的蛋白保存在PBS(58mM Na2HPO4, 17mM NaH2PO4, 68mM NaCl, pH7.4)里,并往里面加入500mM咪唑和10%甘油。
[3].
怎样确定猪循环GMP-AMP合酶(CGAS)重组蛋白的浓度?
蛋白浓度的确定没有一个统一的标准,这主要取决于蛋白的氨基酸序列。伊艾博是根据不同测试的组合来测定蛋白浓度。考马斯亮蓝法、BCA法、氨基酸序列和氨基酸全序列分析法等都用来测定蛋白浓度。
[4].
猪循环GMP-AMP合酶(CGAS)重组蛋白蛋白保存条件是怎样的?
蛋白应保存在 -20℃或 -80℃条件下,为了避免反复冻融,可以将蛋白分装成小份保存。
[5].
猪循环GMP-AMP合酶(CGAS)重组蛋白是否可以用于活体实验?
重组蛋白没有用于任何的活体实验,因此蛋白的活性和半衰期是不确定的。
[6].
猪循环GMP-AMP合酶(CGAS)重组蛋白的保质期是多久?
在适当的保存条件下,从购买之日起蛋白可以稳定保存6-12个月。适当的保存条件是:蛋白保存在-20°C o或 -80℃,保证蛋白的保存浓度高于0.1mg/ml,限制蛋白反复冻融的次数。我们公司常规的质量检测保证所有产品在销售时都有可接受的生物活性。但是我们不能控制终端用户蛋白的保存条件。如果产品在有效期内出现问题,请联系我们的技术支持。
[7].
你们蛋白和抗体的报价是怎么样的?
我们将根据你需要的蛋白和抗体的大小进行报价。
[8].
猪循环GMP-AMP合酶(CGAS)重组蛋白是否能够提供蛋白片段?
我们现有的人的蛋白的序列可以有很多。你可以选择你感兴趣的靶向部分,我们将会按您的需求提供蛋白和抗体。
[9].
猪循环GMP-AMP合酶(CGAS)重组蛋白的货期或发货时间一般是多长?
具体指标的货期需要确定。最快一周,最长可能一个月。
反馈墙
评论数 : 0
所有用户
所有用户
默认排序
默认排序
最近
早期
目前还没有评论。



通知
规格
数量
单价 (¥)
小计 1 (¥)
小计 2:
¥

规格
数量
单价 (¥)





 验证序列:
验证序列:



 折扣:
折扣: